This page shows the slide image in Salari on iPhone, but not in Chrome on PC. I have to change the location of the images, because Latest Chrome does not allow HTTP images to be displayed on HTTPS pages.
slide
 Tokyo Tech MOT Homecoming Day “AI and MOT “2018-05-26Senior Researcher, Cybozu LabsPresident, General Incorporated AssociationFUTO DirectorTokyo Tech MOT 2011Admission-2014Completion2018Specified Associate ProfessorNISHIO Hirokazu
Tokyo Tech MOT Homecoming Day “AI and MOT “2018-05-26Senior Researcher, Cybozu LabsPresident, General Incorporated AssociationFUTO DirectorTokyo Tech MOT 2011Admission-2014Completion2018Specified Associate ProfessorNISHIO Hirokazu
 Facebook Group 2Share lecture materials, questions, comments, and anything else.
Facebook Group 2Share lecture materials, questions, comments, and anything else.
 Objective 3 of this presentation will increase the probability that people who hear this presentation will create economic value.
Objective 3 of this presentation will increase the probability that people who hear this presentation will create economic value.
 AlphaGo 4First Go Program to Beat the Pros
AlphaGo 4First Go Program to Beat the Pros
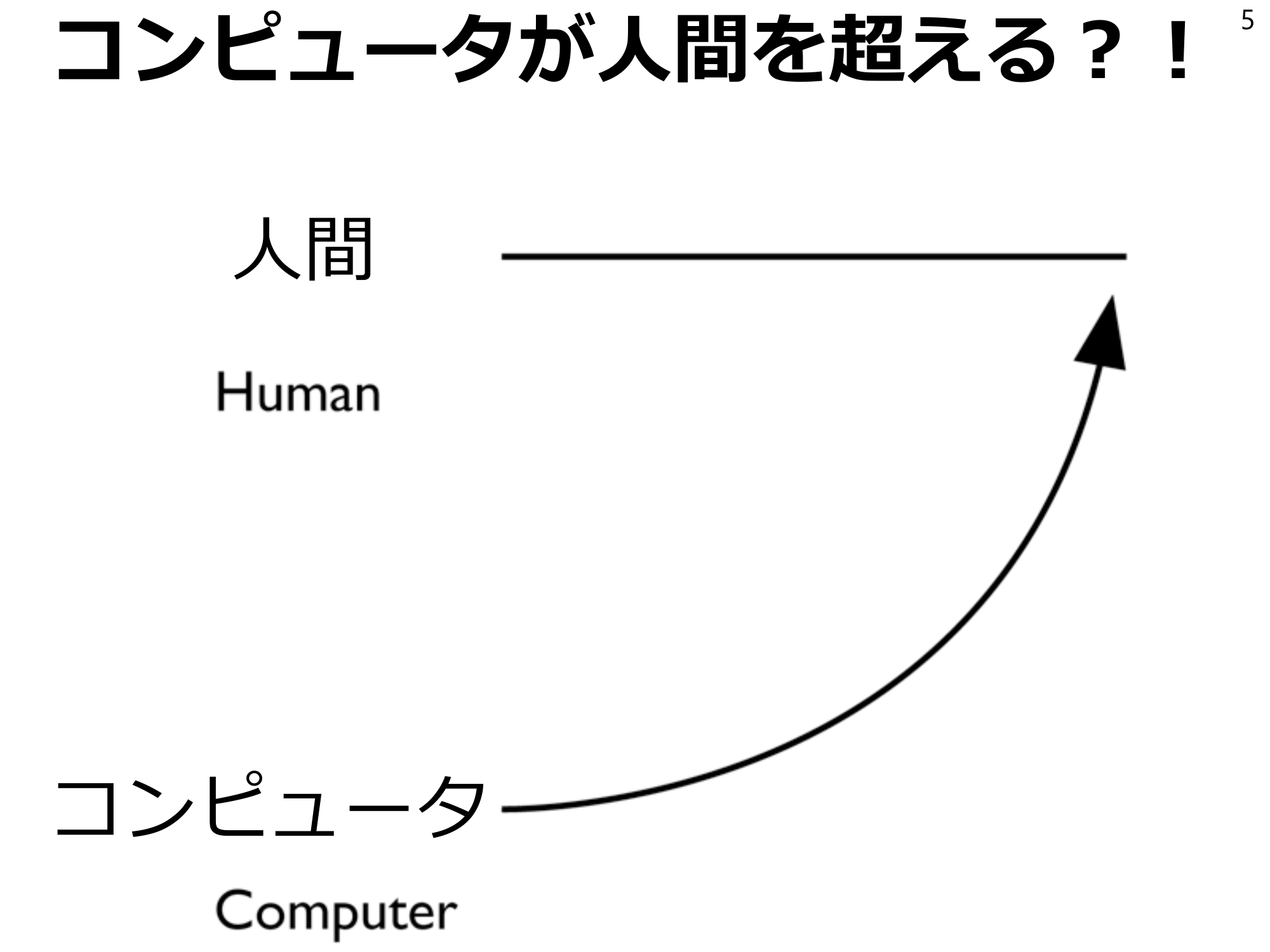 Computers Surpass Humans? 5Human Computers
Computers Surpass Humans? 5Human Computers
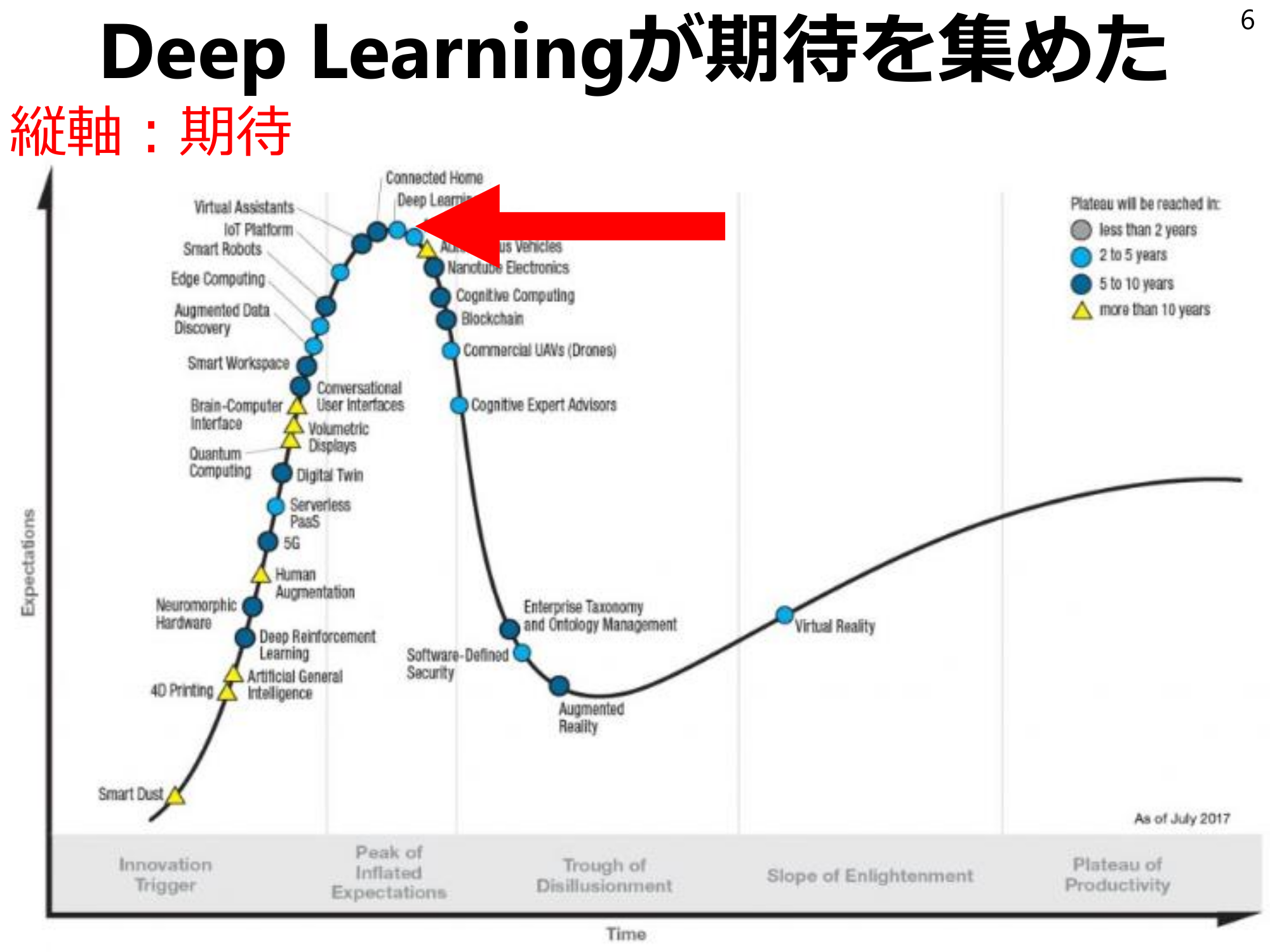 Deep Learning has shown promise6Vertical Axis: Expectations
Deep Learning has shown promise6Vertical Axis: Expectations
 Source display 7 https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-trends-in-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for- emerging-technologies-2017/
Source display 7 https://www.gartner.com/smarterwithgartner/top-trends-in-the-gartner-hype-cycle-for- emerging-technologies-2017/
 8 It seems that Deep Learning, a technology like a magic wand, can solve a lot of problems!
8 It seems that Deep Learning, a technology like a magic wand, can solve a lot of problems!
 Case Study:Predicting Parking Difficulty9 https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/02/using-machine-learning-to-predict.html
Case Study:Predicting Parking Difficulty9 https://ai.googleblog.com/2017/02/using-machine-learning-to-predict.html
 Parking Difficulty Prediction 10 - Google Maps feature - “How hard is it to park in this area at this time? Easy?” -Deep Learning is amazing!
Parking Difficulty Prediction 10 - Google Maps feature - “How hard is it to park in this area at this time? Easy?” -Deep Learning is amazing!
 We did not use Deep Learning11 “We used logistic regression” Reasons (excerpts) -Easy to understand the behavior -High tolerance to noise -Easy to verify that the model is working properly
We did not use Deep Learning11 “We used logistic regression” Reasons (excerpts) -Easy to understand the behavior -High tolerance to noise -Easy to verify that the model is working properly
 Logistic regression12 -Method created in 1958 -Mathematically equivalent to thin neural nets, not Deep Learning -Will be a dead method, so learning is getting faster
Logistic regression12 -Method created in 1958 -Mathematically equivalent to thin neural nets, not Deep Learning -Will be a dead method, so learning is getting faster
 Survey by Kaggle13A large survey conducted by Kaggle, the largest machine learning competition, asked 7301 data scientists what machine learning methods they use in their work…The State of ML and Data Science 2017 | Kaggle https://www.kaggle.com/surveys/2017
Survey by Kaggle13A large survey conducted by Kaggle, the largest machine learning competition, asked 7301 data scientists what machine learning methods they use in their work…The State of ML and Data Science 2017 | Kaggle https://www.kaggle.com/surveys/2017
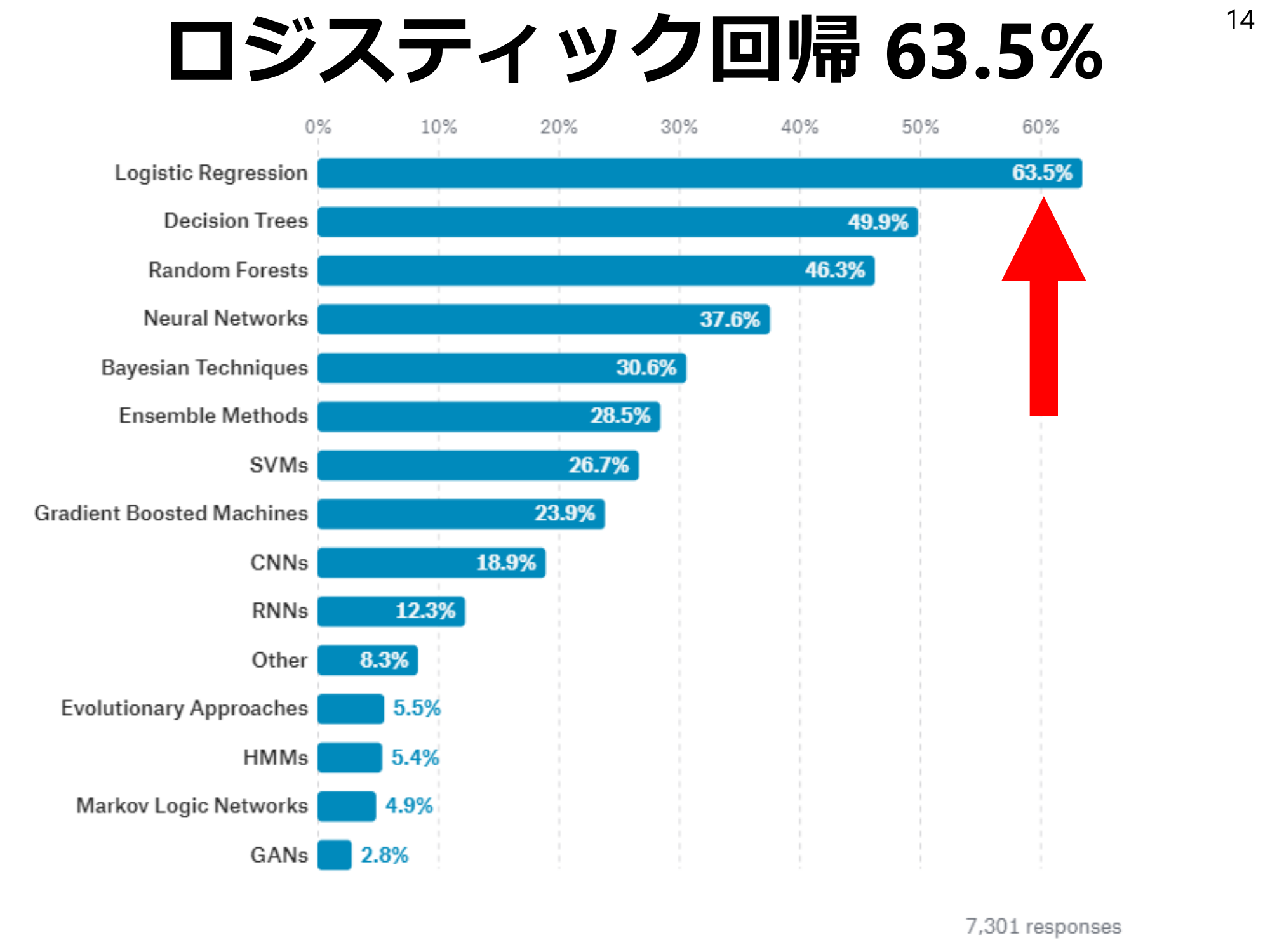 Logistic regression 63.5% 14
Logistic regression 63.5% 14
 The purpose of the means15 -Deep Learning is certainly more accurate than past methods for certain tasks, but it is not a universal tool nor is it a magic wand. Let’s improve business management with Deep Learning” is wrong because the tool is decided before the objective is decided.
The purpose of the means15 -Deep Learning is certainly more accurate than past methods for certain tasks, but it is not a universal tool nor is it a magic wand. Let’s improve business management with Deep Learning” is wrong because the tool is decided before the objective is decided.
 AlphaGo 16 - I want you to get a rough sense of the scale - I’ll explain in a bit more detail - I won’t explain the differences between the detailed versions.
AlphaGo 16 - I want you to get a rough sense of the scale - I’ll explain in a bit more detail - I won’t explain the differences between the detailed versions.
 Amount of data: 28.4 million data from 160,000 games obtained from 17 Go online match servers.
Amount of data: 28.4 million data from 160,000 games obtained from 17 Go online match servers.
 Learning Results 18Able to guess the human “next move” with a 57.0% correct answer rate.
Learning Results 18Able to guess the human “next move” with a 57.0% correct answer rate.
 Generate data through self-play19Machines play 30 million games against each other because the 160,000 game data generated by human games is not enough (using the characteristics of Go, which allows data to be collected without the intervention of humans or the physical world).
Generate data through self-play19Machines play 30 million games against each other because the 160,000 game data generated by human games is not enough (using the characteristics of Go, which allows data to be collected without the intervention of humans or the physical world).
 30 million games is about 1 hour per game for 20 people, so 3500 years (sleepless nights).
30 million games is about 1 hour per game for 20 people, so 3500 years (sleepless nights).
 21The exact amount of money spent on the study is, of course, unknown, but based on publicly available information, it is estimated to be about 3 billion yen. 058.html
21The exact amount of money spent on the study is, of course, unknown, but based on publicly available information, it is estimated to be about 3 billion yen. 058.html
 Summary 22 - First, collect about 30 million data of “decisions made by humans” - Collect 200 times more data by simulation - Invest 3 billion yen in this process
Summary 22 - First, collect about 30 million data of “decisions made by humans” - Collect 200 times more data by simulation - Invest 3 billion yen in this process
 23Why did you do it? (Let’s think about it from a manager’s perspective)
23Why did you do it? (Let’s think about it from a manager’s perspective)
 Why play AlphaGo? 24 - Branding? -To train new employees? -Because it’s a world first and it gets employees excited? -To attract investment by showing dreams?
Why play AlphaGo? 24 - Branding? -To train new employees? -Because it’s a world first and it gets employees excited? -To attract investment by showing dreams?
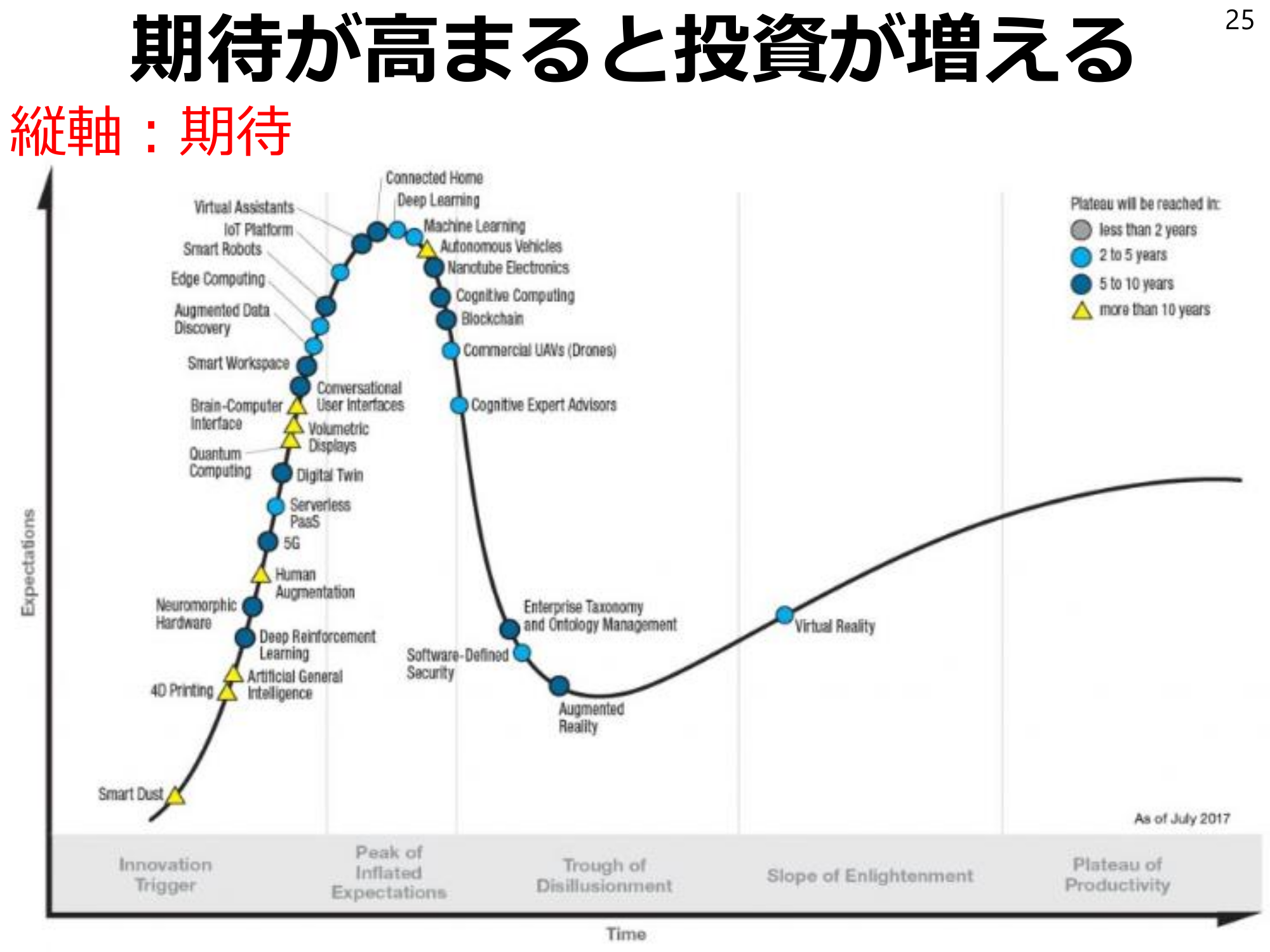 Investment increases as expectations increase25Vertical Axis: Expectations
Investment increases as expectations increase25Vertical Axis: Expectations
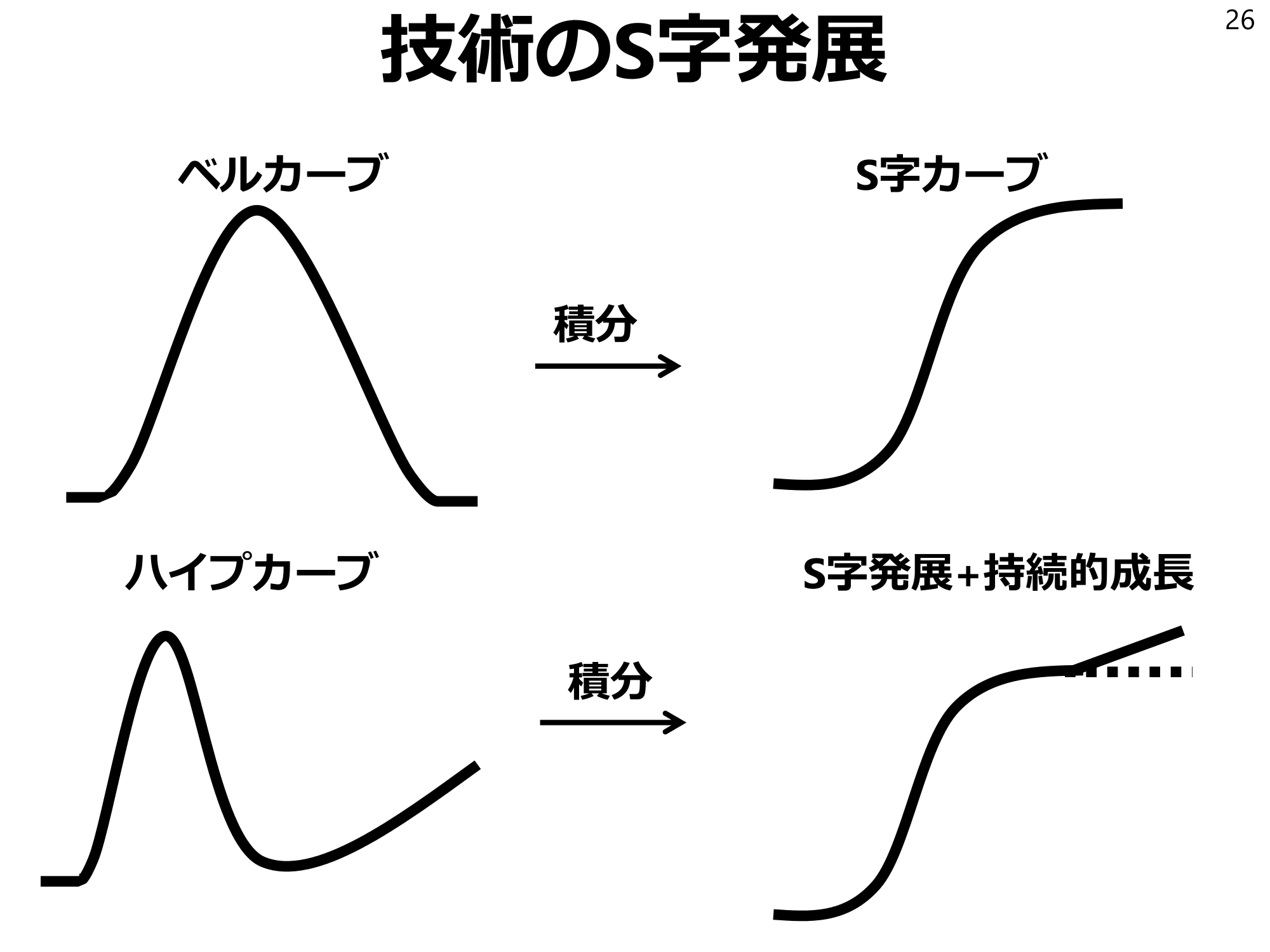 S-curve development of technology 26 bell curve S-curve integral hype curve S-curve development + sustainable growth integral
S-curve development of technology 26 bell curve S-curve integral hype curve S-curve development + sustainable growth integral
 Self-fulfillment of the prophecy27 -Promoting the awesomeness of the technology -Expectations for the future are raised -Investment is drawn out -This increases the speed of technological progress.
Self-fulfillment of the prophecy27 -Promoting the awesomeness of the technology -Expectations for the future are raised -Investment is drawn out -This increases the speed of technological progress.
 28But also counterproductive…
28But also counterproductive…
 29 Fear of losing jobs to AI
29 Fear of losing jobs to AI
 30 Knowledge is the Antidote to Fear Ralph Waldo Emerson “Society and Solitude”
30 Knowledge is the Antidote to Fear Ralph Waldo Emerson “Society and Solitude”
 31Based on concrete examples, not vague concepts
31Based on concrete examples, not vague concepts
 Case Study: Miura City Agricultural Cooperative’s Scheduled Dispatch System32 ref: ICT Changes Society Case Study
Case Study: Miura City Agricultural Cooperative’s Scheduled Dispatch System32 ref: ICT Changes Society Case Study
 33 “Eight hours of shipping work reduced to one second”: the amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
33 “Eight hours of shipping work reduced to one second”: the amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
 Algorithm eliminates 8h of work34 --- “Creating a delivery schedule for shipments, one of the most troublesome tasks in agricultural cooperative operations” “A task that used to take 8 hours a day takes only 1 second. “Unique algorithm” I created this algorithm. The amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: “From 8 hours of shipping work to 1 second.” http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
Algorithm eliminates 8h of work34 --- “Creating a delivery schedule for shipments, one of the most troublesome tasks in agricultural cooperative operations” “A task that used to take 8 hours a day takes only 1 second. “Unique algorithm” I created this algorithm. The amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: “From 8 hours of shipping work to 1 second.” http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
 “Creating a delivery schedule “35 - “We figure out how much of the shipment is going to be shipped from the farmers the next day, and determine the quantity to be shipped to each destination, such as a market, and how to distribute the cargo to the trucks of which carriers.” -The creation of a truck dispatch schedule takes a mid-level staff member eight hours and a veteran 56 hours. -Young staff “can’t do this as expected,” “8 hours of shipping work to 1 second” -An amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
“Creating a delivery schedule “35 - “We figure out how much of the shipment is going to be shipped from the farmers the next day, and determine the quantity to be shipped to each destination, such as a market, and how to distribute the cargo to the trucks of which carriers.” -The creation of a truck dispatch schedule takes a mid-level staff member eight hours and a veteran 56 hours. -Young staff “can’t do this as expected,” “8 hours of shipping work to 1 second” -An amazing evolution that took place at the Miura City Agricultural Cooperative: http://wedge.ismedia.jp/articles/-/12062
 Is it bad that “AI is taking away our jobs? Masayoshi Iijima, assistant general manager of the cooperative’s sales department, commented positively, “The biggest thing is the reduction in working hours. I have high expectations for the new system because it will reduce the workload of the staff and they can use their free time more efficiently for sales and other activities,” he said.
Is it bad that “AI is taking away our jobs? Masayoshi Iijima, assistant general manager of the cooperative’s sales department, commented positively, “The biggest thing is the reduction in working hours. I have high expectations for the new system because it will reduce the workload of the staff and they can use their free time more efficiently for sales and other activities,” he said.
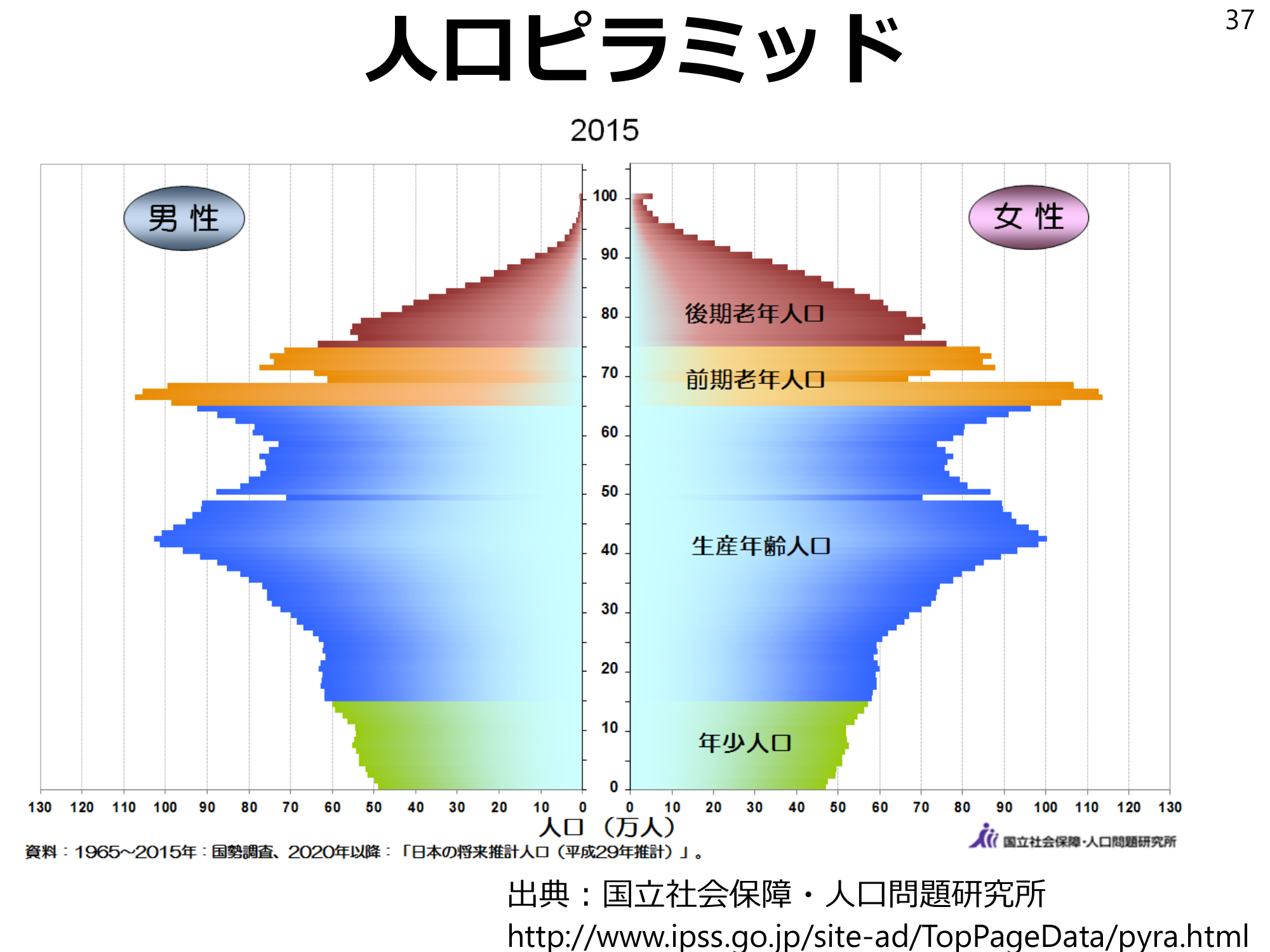 Population pyramid37 Source: National Institute of Population and Social Security Research http://www.ipss.go.jp/site-ad/TopPageData/pyra.html
Population pyramid37 Source: National Institute of Population and Social Security Research http://www.ipss.go.jp/site-ad/TopPageData/pyra.html
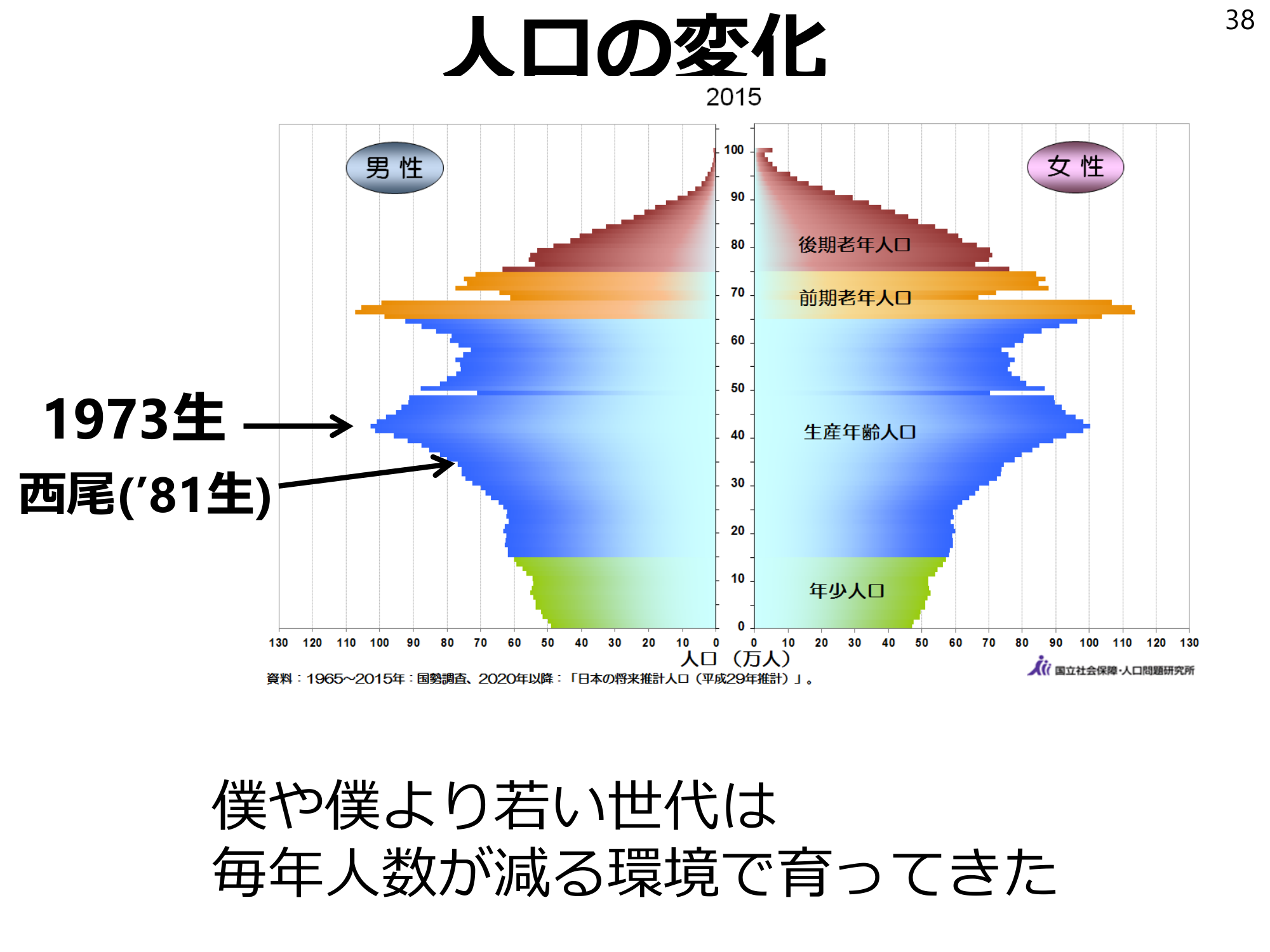 Population Change38 Nishio, b. 1973 (‘81) I and the generation younger than me grew up in an environment where the number of people decreased every year.
Population Change38 Nishio, b. 1973 (‘81) I and the generation younger than me grew up in an environment where the number of people decreased every year.
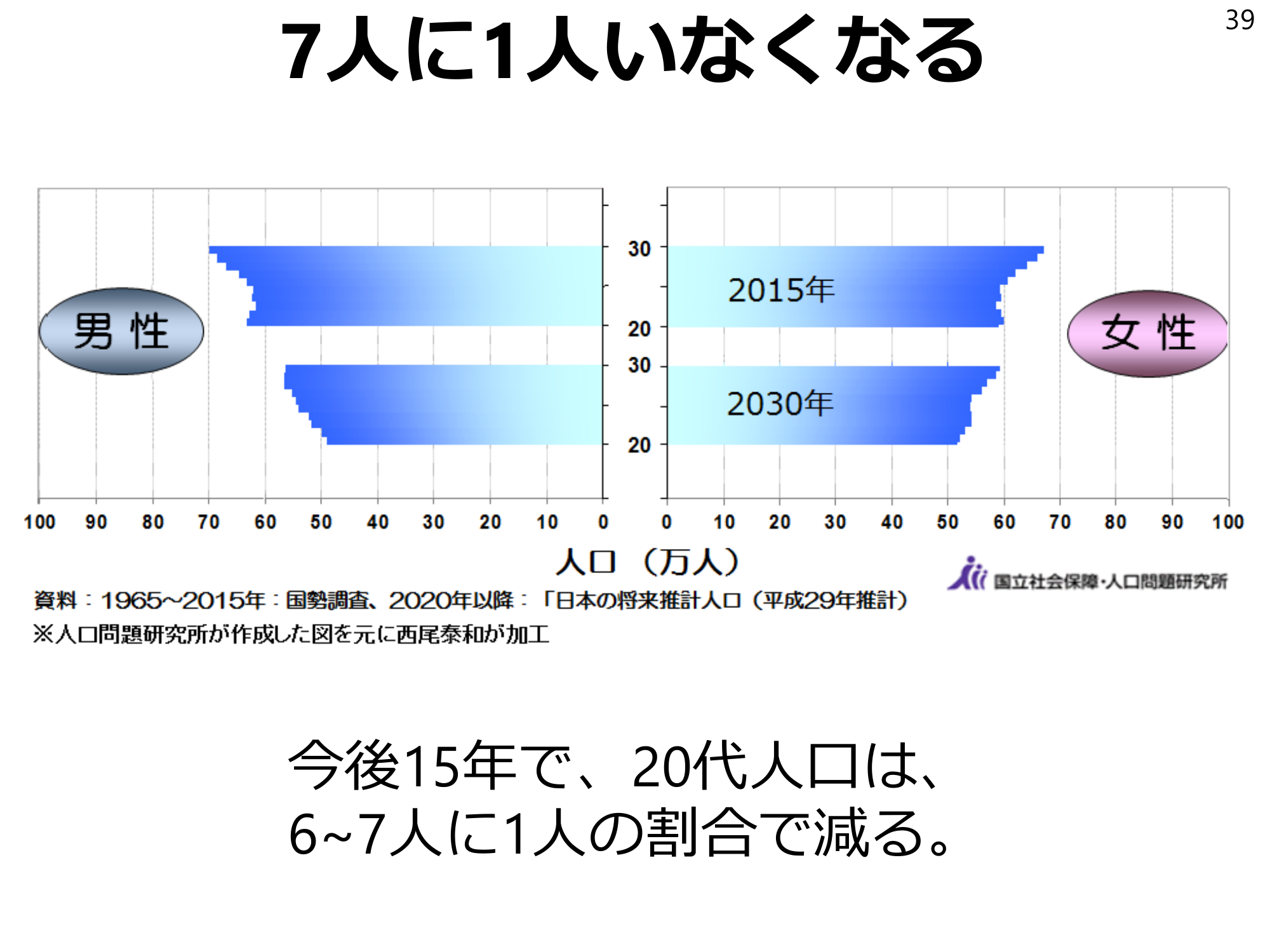 One in seven will be gone.39 Over the next 15 years, the 20-something population will decline by one in 67.
One in seven will be gone.39 Over the next 15 years, the 20-something population will decline by one in 67.
 If one person in seven disappears…40 The work that is being done by a team of seven now must be done by six people in 15 years if the age structure of the team remains the same If the workload remains the same, the workload per person will increase by 17% for a job that is worked 20 days a month x 8 hours a month with a 17% increase in workload. +27 hours per month. Overtime +1 hour every day or -3 days off every month.
If one person in seven disappears…40 The work that is being done by a team of seven now must be done by six people in 15 years if the age structure of the team remains the same If the workload remains the same, the workload per person will increase by 17% for a job that is worked 20 days a month x 8 hours a month with a 17% increase in workload. +27 hours per month. Overtime +1 hour every day or -3 days off every month.
 Maintaining the status quo is 41 “doing the same job the same way we have always done it” is not maintaining the status quo. It is not maintaining the status quo, because the burden on humans will increase and they will not be able to do their jobs. To maintain the status quo, 1/7 of the work must be “taken away by AI” or human capacity must be increased by 7/6.
Maintaining the status quo is 41 “doing the same job the same way we have always done it” is not maintaining the status quo. It is not maintaining the status quo, because the burden on humans will increase and they will not be able to do their jobs. To maintain the status quo, 1/7 of the work must be “taken away by AI” or human capacity must be increased by 7/6.
 42 x AI will take 1/7th of the work ○ AI will take 1/7th of the work off our shoulders ○ AI will be used to augment humans by 16
42 x AI will take 1/7th of the work ○ AI will take 1/7th of the work off our shoulders ○ AI will be used to augment humans by 16
 Reinvestment of excess time43 -Trend of fewer young people -Hiring new people is slowly becoming more difficult -The idea of “reducing jobs with AI and laying off excess workers” is a bad idea -Reduce jobs with AI and and reinvest the free time created into more productive jobs - Expand and reproduce
Reinvestment of excess time43 -Trend of fewer young people -Hiring new people is slowly becoming more difficult -The idea of “reducing jobs with AI and laying off excess workers” is a bad idea -Reduce jobs with AI and and reinvest the free time created into more productive jobs - Expand and reproduce
 human computer
human computer
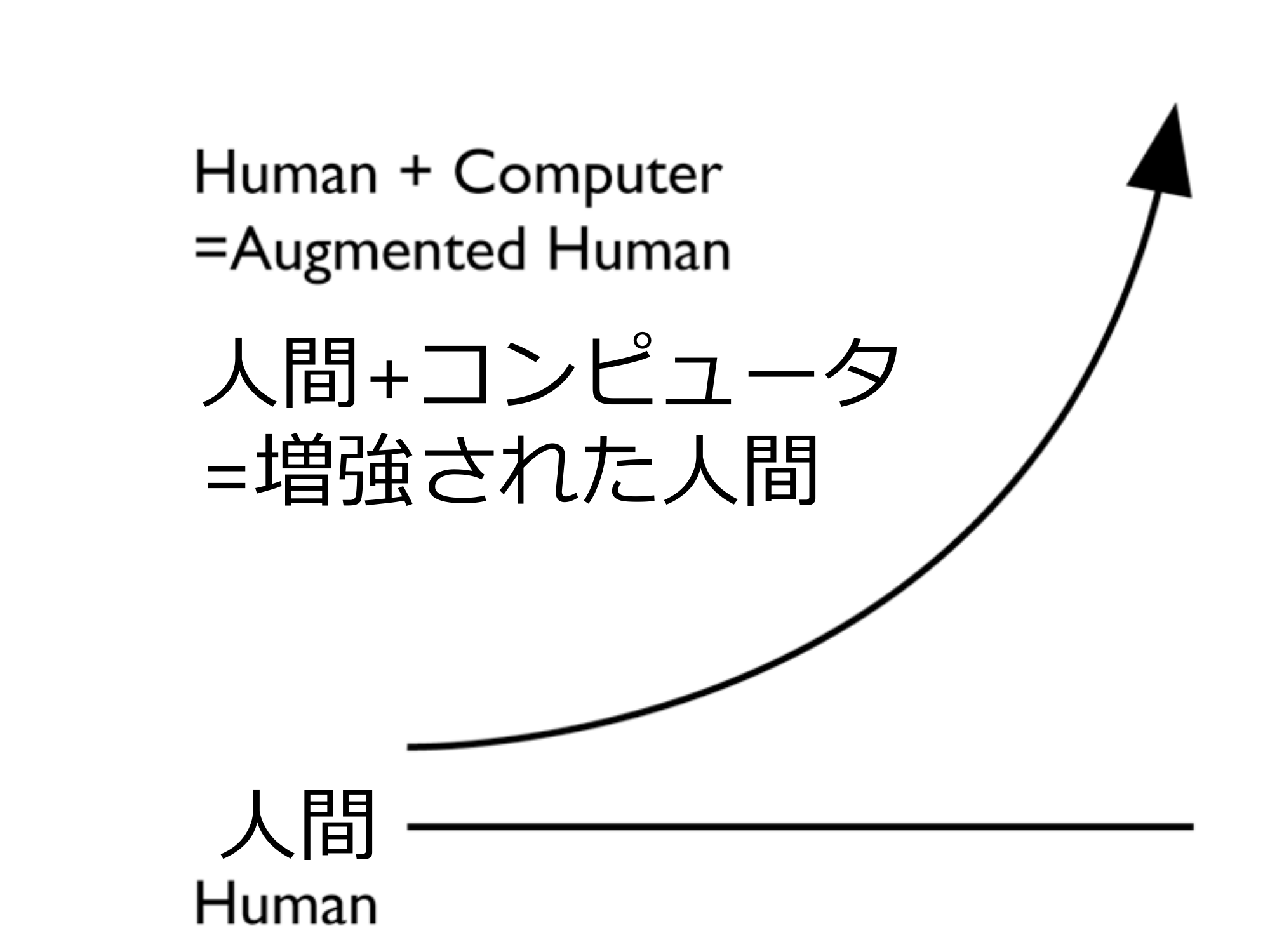
- Human + computer = augmented human human being
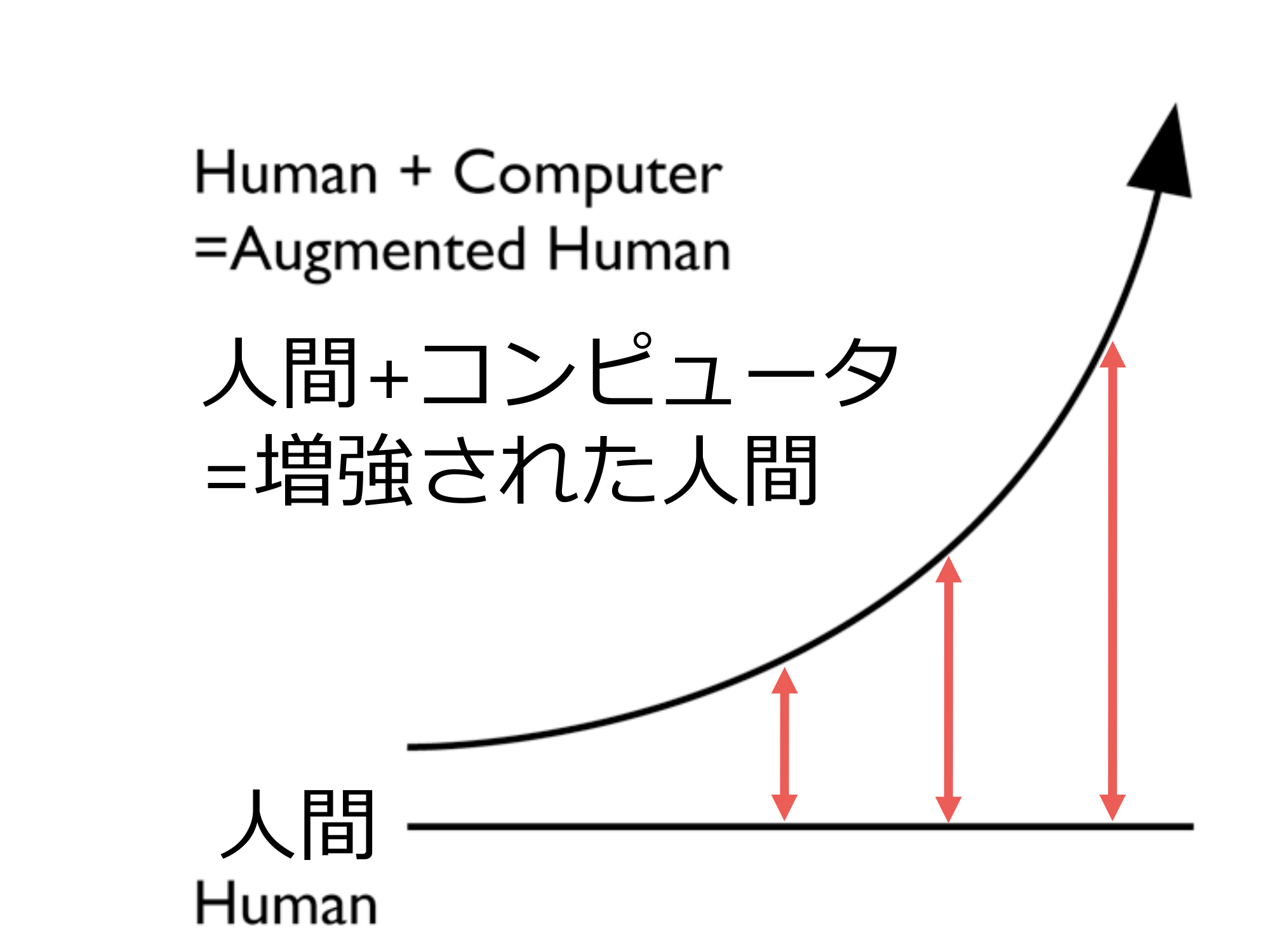 Human + computer = augmented human human human
Human + computer = augmented human human human
 Examples of Enhancement47 -Computing power enhancement by computer -Transmission power enhancement by internet -Information discovery power enhancement by search engines Here are some more examples
Examples of Enhancement47 -Computing power enhancement by computer -Transmission power enhancement by internet -Information discovery power enhancement by search engines Here are some more examples
 Automated Programming48The idea is to automate programming because it is hard to program.
Automated Programming48The idea is to automate programming because it is hard to program.
 Before automatic programming49I want to do “add A and B and put them in C.” LOAD 1 ADD 2 STORE 3Load the value in memory 1 to the temporary area for calculationAdd the value in memory 2 to itAdd the value in memory 3 to the temporary areaThis is pseudo code to make things simple, In reality, it is much more complicated.
Before automatic programming49I want to do “add A and B and put them in C.” LOAD 1 ADD 2 STORE 3Load the value in memory 1 to the temporary area for calculationAdd the value in memory 2 to itAdd the value in memory 3 to the temporary areaThis is pseudo code to make things simple, In reality, it is much more complicated.
 Automatic Programming 50 “Add A and B to C” is written in the notation C = A + B;. The computer reads this notation and automatically generates LOAD 1; ADD 2; STORE 3; “Formula Conversion System”.
Automatic Programming 50 “Add A and B to C” is written in the notation C = A + B;. The computer reads this notation and automatically generates LOAD 1; ADD 2; STORE 3; “Formula Conversion System”.
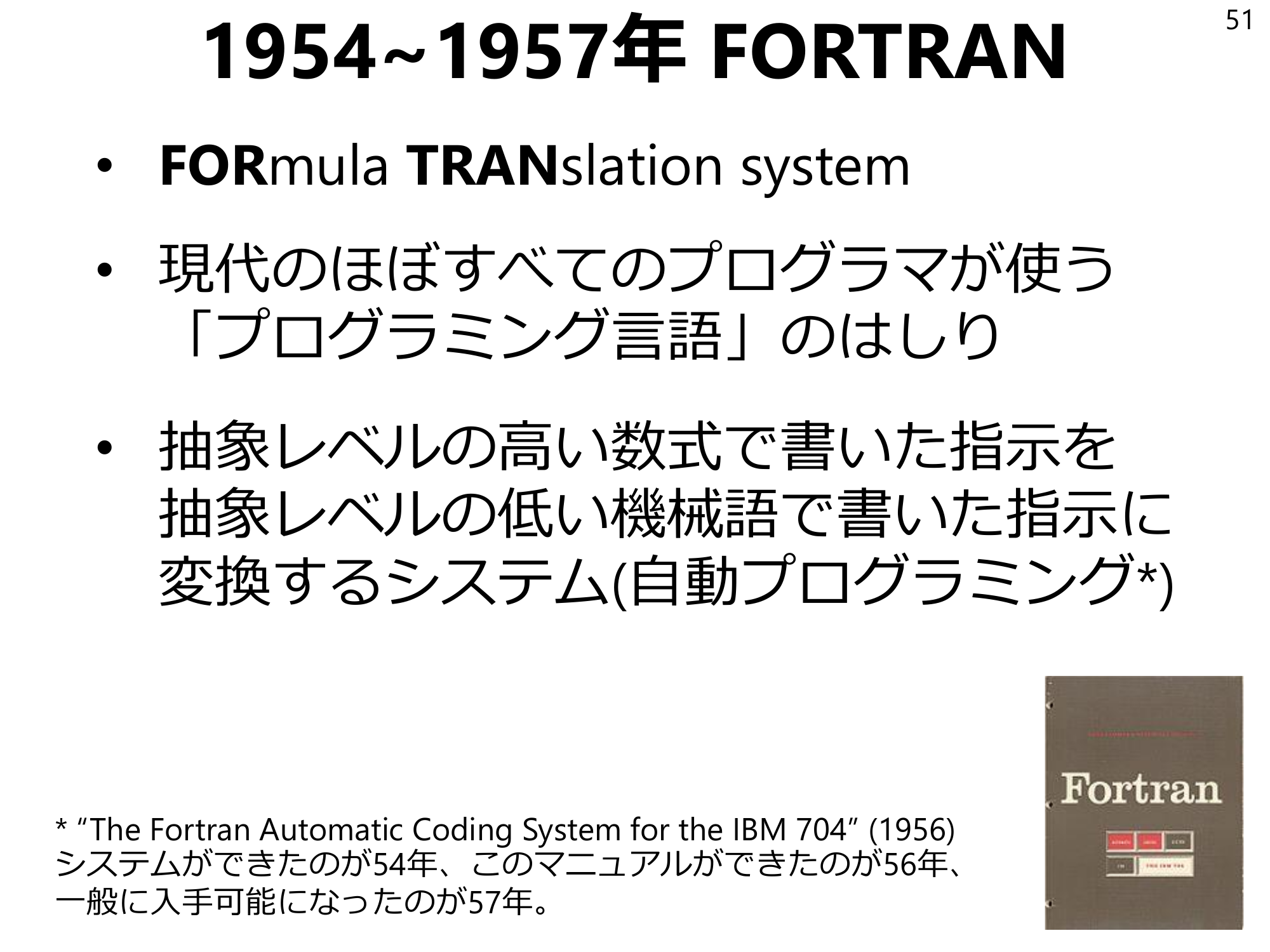 19541957 FORTRAN 51 -FORmula TRANslation system -the beginning of the “programming language” used by almost all modern programmers - a system for converting instructions written in mathematical expressions at a high level of abstraction into instructions written in machine language at a low level of abstraction (automatic programming*). System for converting instructions written in mathematical formulas at a high level of abstraction into instructions written in machine language at a low level of abstraction (automatic programming*) *“The Fortran Automatic Coding System for the IBM 704” (1956)The system was created in 1954, and this manual was created in 1956, and became available to the public in 1956. 56, and it became generally available in 57.
19541957 FORTRAN 51 -FORmula TRANslation system -the beginning of the “programming language” used by almost all modern programmers - a system for converting instructions written in mathematical expressions at a high level of abstraction into instructions written in machine language at a low level of abstraction (automatic programming*). System for converting instructions written in mathematical formulas at a high level of abstraction into instructions written in machine language at a low level of abstraction (automatic programming*) *“The Fortran Automatic Coding System for the IBM 704” (1956)The system was created in 1954, and this manual was created in 1956, and became available to the public in 1956. 56, and it became generally available in 57.
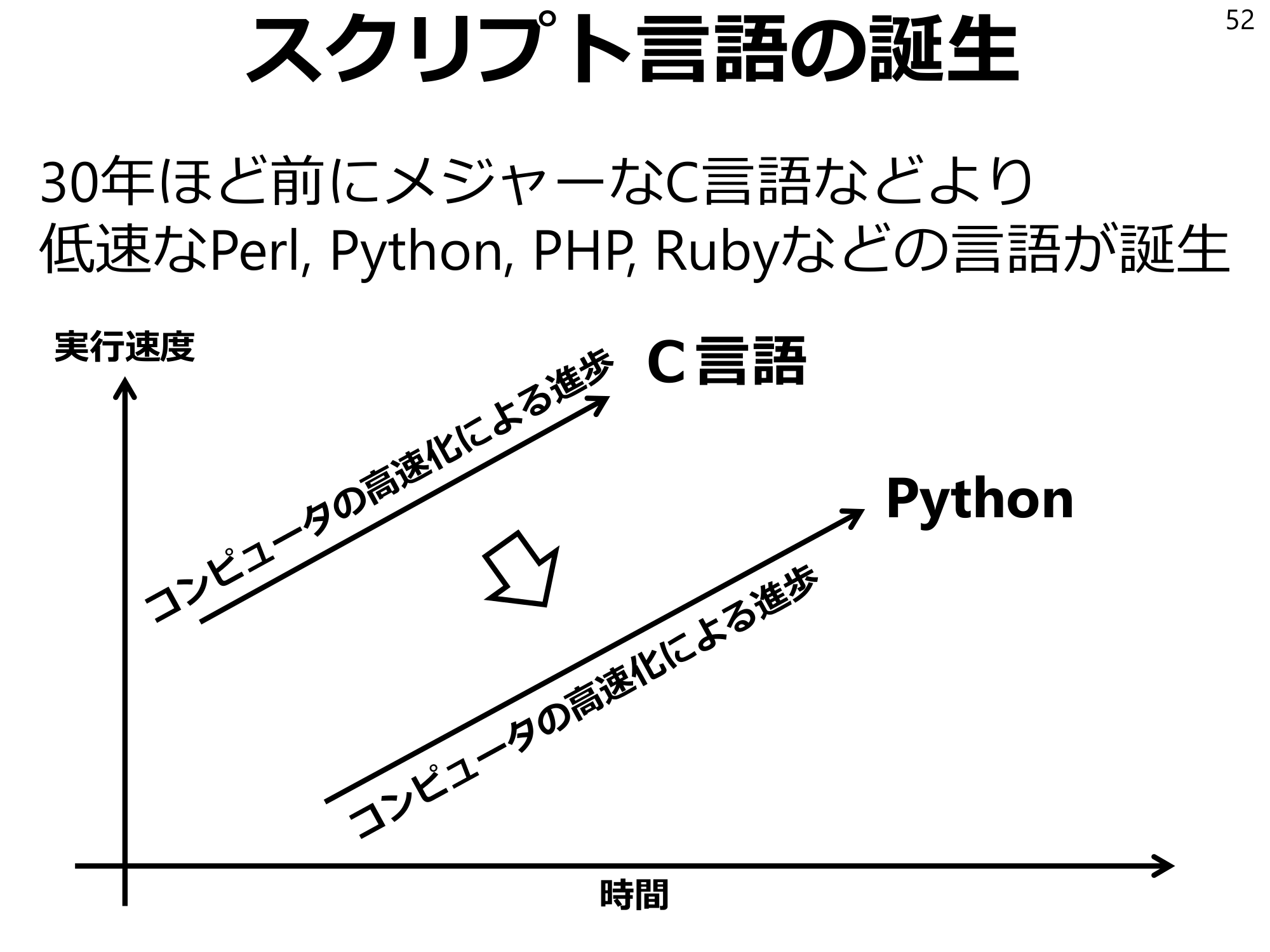 The Birth of Scripting Languages52 About 30 years ago, languages such as Perl, Python, PHP, and Ruby were born, which are slower than major languages such as C. The execution speed C Python time
The Birth of Scripting Languages52 About 30 years ago, languages such as Perl, Python, PHP, and Ruby were born, which are slower than major languages such as C. The execution speed C Python time
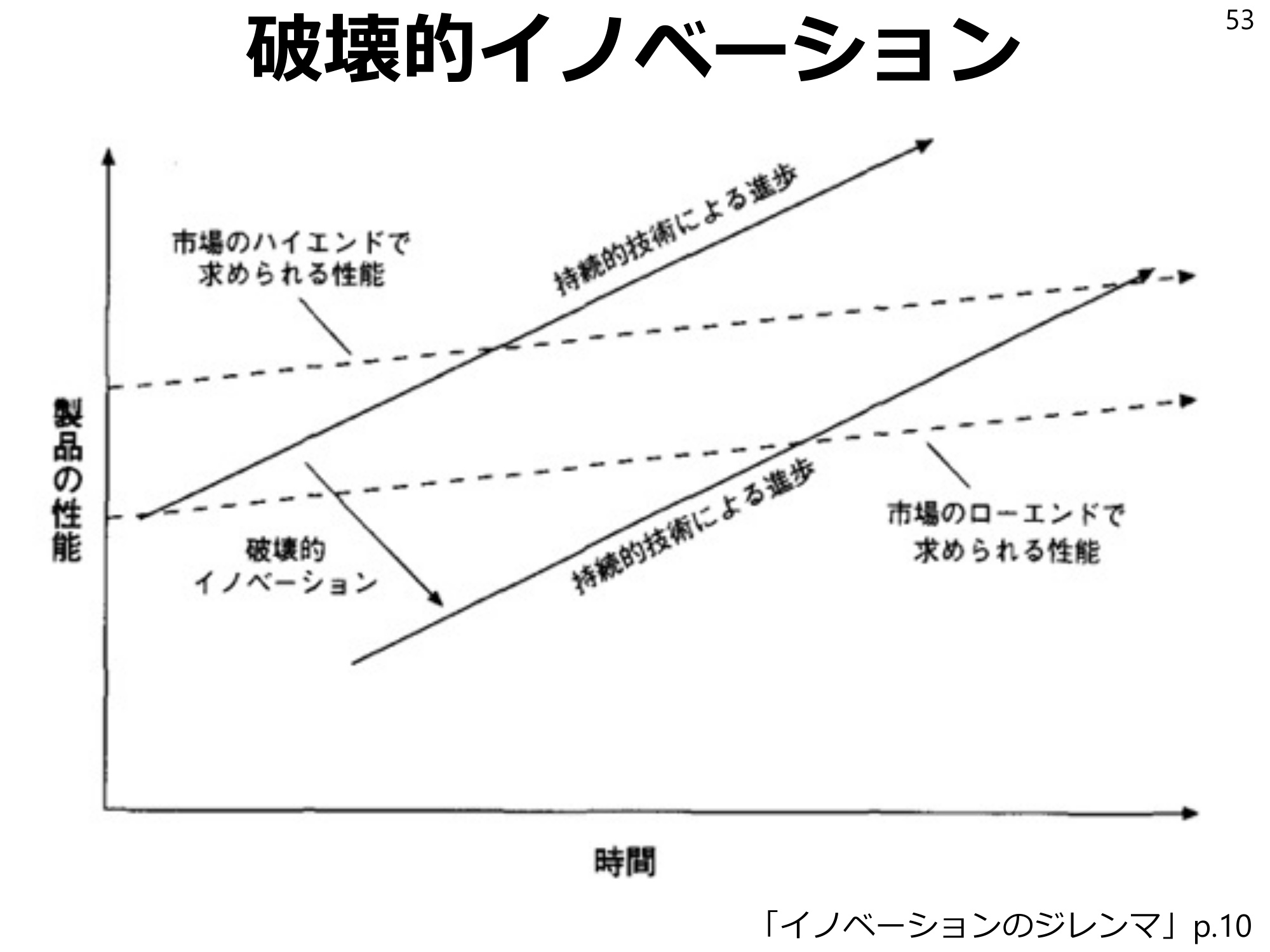 Disruptive Innovation 53 “The Innovation Dilemma,” p. 10
Disruptive Innovation 53 “The Innovation Dilemma,” p. 10
 Scripting languages54 -Computers became faster -Slower programming languages could meet customer demand - “slower to execute, but less time-consuming to implement” Scribble-like languages Scribble-like language with “slow execution but little time for implementation
Scripting languages54 -Computers became faster -Slower programming languages could meet customer demand - “slower to execute, but less time-consuming to implement” Scribble-like languages Scribble-like language with “slow execution but little time for implementation
 Impact of Machine Learning55 -The majority of programs are conditional decisions - humans clarify “what the conditions are” and communicate them to the computer - but some tasks are difficult to “clarify the conditions” (Go, image recognition…) -Machine learning is.., …) - Machine learning is…
Impact of Machine Learning55 -The majority of programs are conditional decisions - humans clarify “what the conditions are” and communicate them to the computer - but some tasks are difficult to “clarify the conditions” (Go, image recognition…) -Machine learning is.., …) - Machine learning is…
 Impact of Machine Learning56Machine learning is a method that allows computers to make conditional judgments by giving them data that represents a situation and “how a human would make a decision in that situation” to learn, without the human having to clarify the conditions. Note: This explanation is limited to supervised learning.
Impact of Machine Learning56Machine learning is a method that allows computers to make conditional judgments by giving them data that represents a situation and “how a human would make a decision in that situation” to learn, without the human having to clarify the conditions. Note: This explanation is limited to supervised learning.
 Reduce cost at the expense of certainty57 - Since humans do not clarify conditions, it is meaningless to ask, “Does it work according to the conditions? The question “Does it work according to the conditions?” is meaningless because the human does not clarify the conditions - “90% of the verification data can be judged as correct” is all that can be said - Reduce the cost of writing the specification at the expense of certainty.
Reduce cost at the expense of certainty57 - Since humans do not clarify conditions, it is meaningless to ask, “Does it work according to the conditions? The question “Does it work according to the conditions?” is meaningless because the human does not clarify the conditions - “90% of the verification data can be judged as correct” is all that can be said - Reduce the cost of writing the specification at the expense of certainty.
 Summary 58 - Automated Programming - Scripting Languages - Machine Learning Commonality is Reduction of Human Costs
Summary 58 - Automated Programming - Scripting Languages - Machine Learning Commonality is Reduction of Human Costs
 Academia and Business Perspectives59From a business perspective - the decrease in costs - new goods and their production methods - enter the “commercially feasible range”.
Academia and Business Perspectives59From a business perspective - the decrease in costs - new goods and their production methods - enter the “commercially feasible range”.
 Difference between Academia and Business60Academia - Data is publicly available - Dead technologies have been investigated long ago - Businesses compete for accuracy by inventing new methods - Data is not publicly available Business - data is not publicly available
Difference between Academia and Business60Academia - Data is publicly available - Dead technologies have been investigated long ago - Businesses compete for accuracy by inventing new methods - Data is not publicly available Business - data is not publicly available
 Business Evaluation Axis 61Customer ValueNot Newness
Business Evaluation Axis 61Customer ValueNot Newness
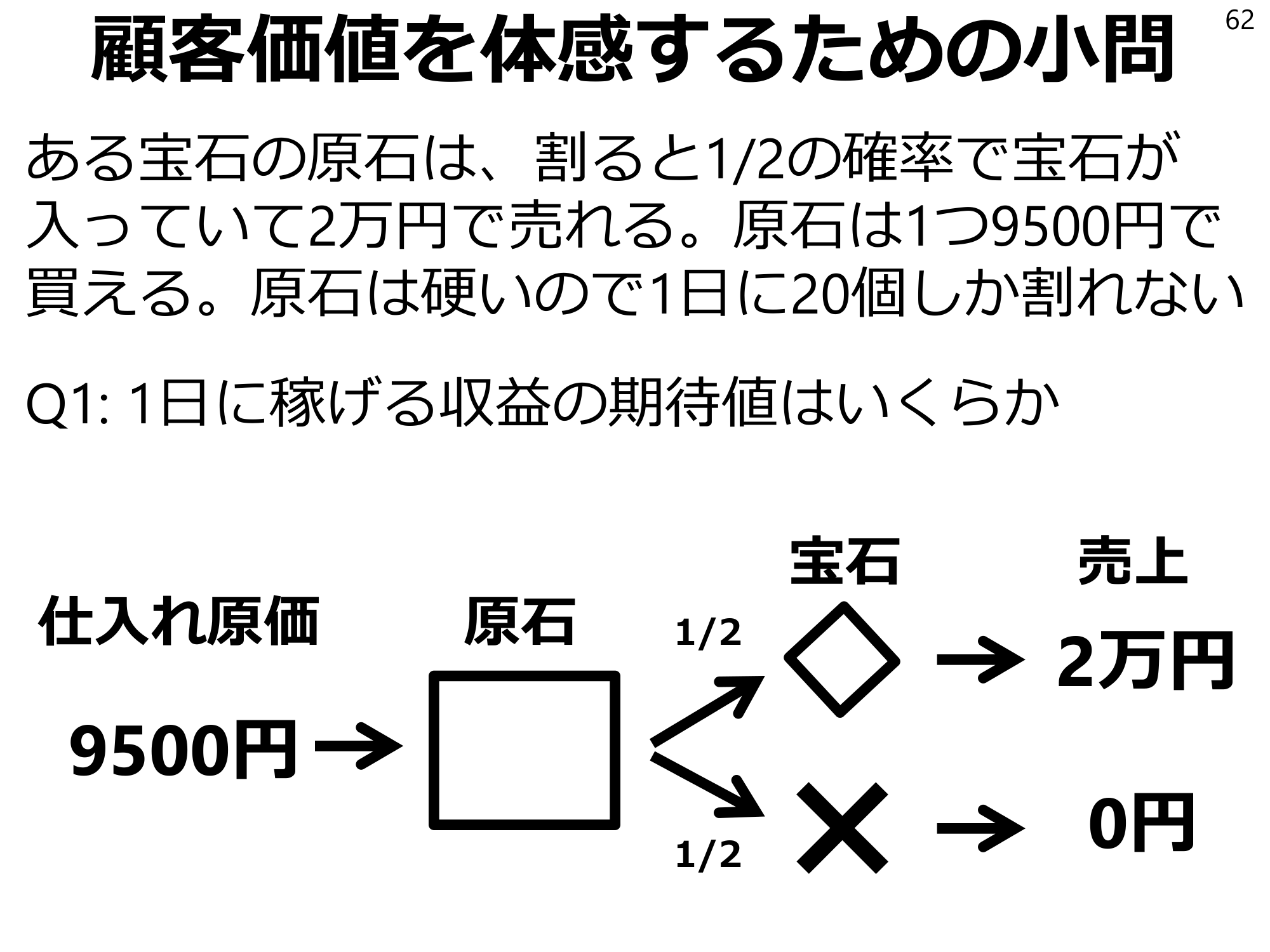 Sub-question 62 for experiencing customer value: A gemstone, which has a 1/2 chance of containing a gem when broken, sells for 20,000 yen. One rough gemstone costs 9,500 yen. Since the gemstone is hard, only 20 pieces can be broken per day.Q1: What is the expected value of revenue that can be earned per day? Purchase cost1/2 gemstone9500 yen x 1/2 sales20,000 yen0 yen
Sub-question 62 for experiencing customer value: A gemstone, which has a 1/2 chance of containing a gem when broken, sells for 20,000 yen. One rough gemstone costs 9,500 yen. Since the gemstone is hard, only 20 pieces can be broken per day.Q1: What is the expected value of revenue that can be earned per day? Purchase cost1/2 gemstone9500 yen x 1/2 sales20,000 yen0 yen
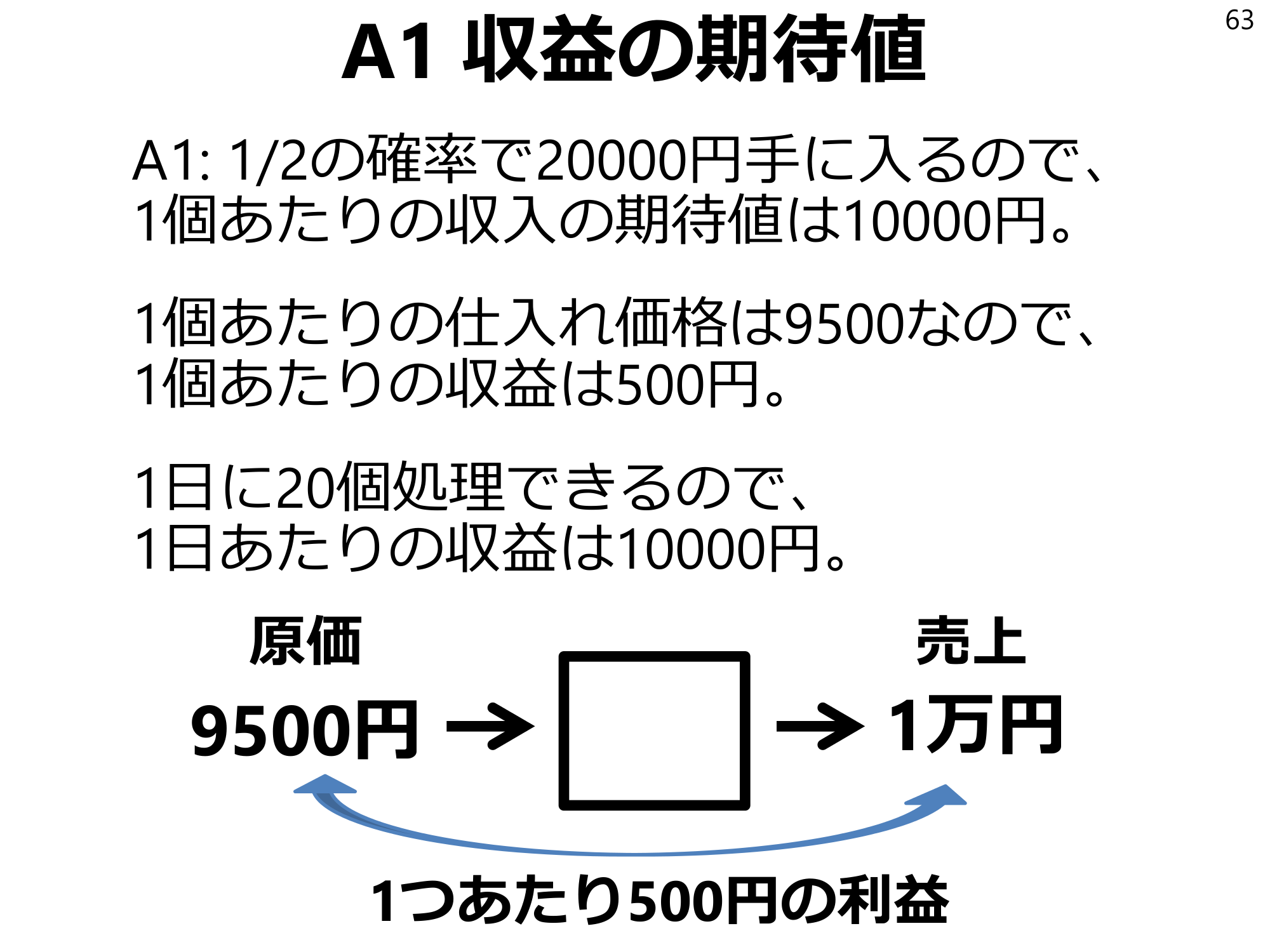 A1Expected value of earnings63 A1: Since there is a 1/2 chance of getting 20,000 yen, the expected value of earnings per unit is 10,000 yen. 9500 is the purchase price per unit, so earnings per unit is 500 yen. 20 units can be processed per day, so earnings per day is 10,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yen sales 10,000 yen profit of 500 yen per unit.
A1Expected value of earnings63 A1: Since there is a 1/2 chance of getting 20,000 yen, the expected value of earnings per unit is 10,000 yen. 9500 is the purchase price per unit, so earnings per unit is 500 yen. 20 units can be processed per day, so earnings per day is 10,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yen sales 10,000 yen profit of 500 yen per unit.
 Q2Double processing speed device64 Q2: Suppose you have a machine that breaks rough stones at twice the speed of a human. In other words, the number of rough stones that can be broken per day increases from 20 to 40. How much would the expected value of revenue increase?
Q2Double processing speed device64 Q2: Suppose you have a machine that breaks rough stones at twice the speed of a human. In other words, the number of rough stones that can be broken per day increases from 20 to 40. How much would the expected value of revenue increase?
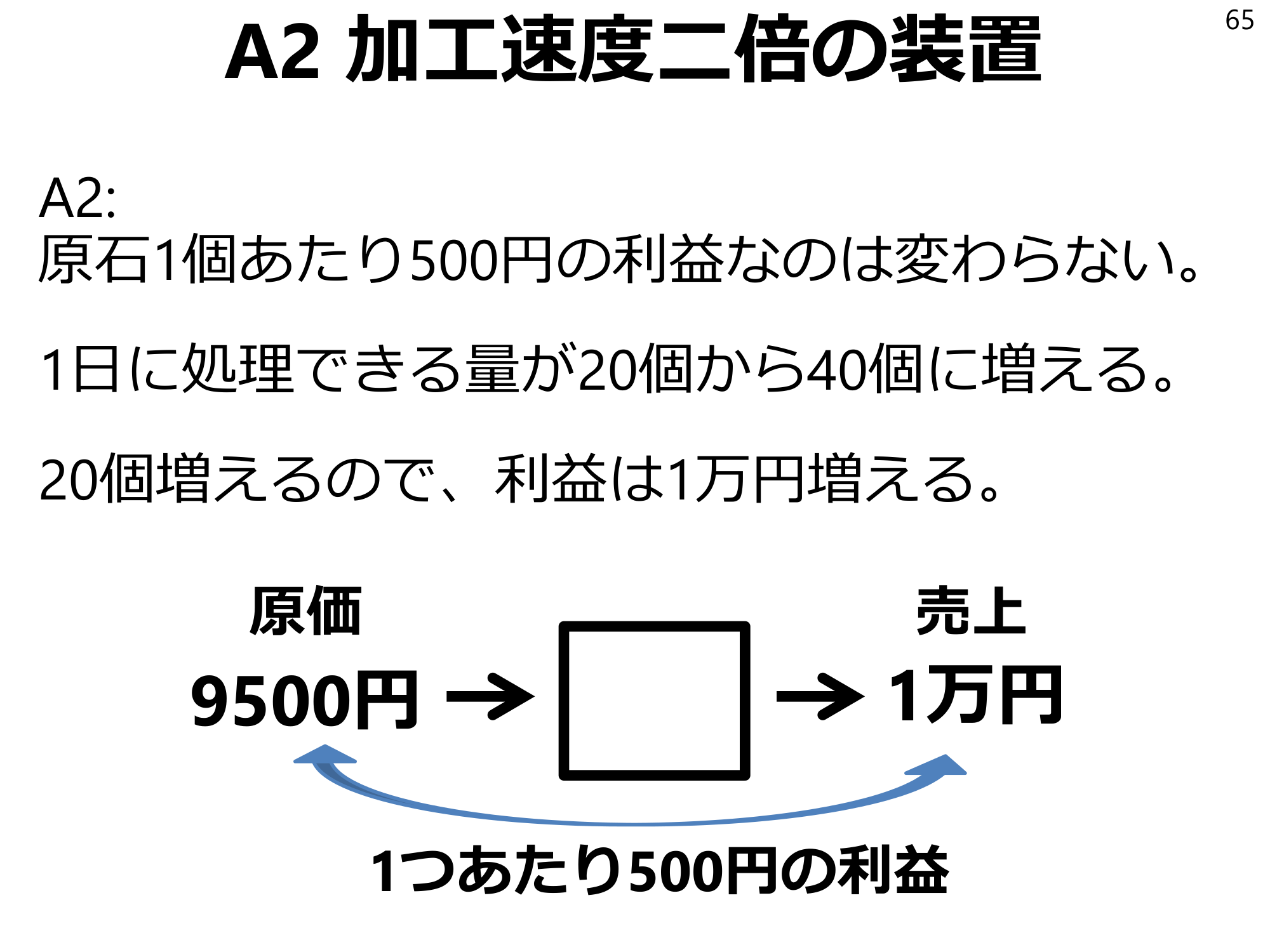 A2: The profit of 500 yen per rough stone remains the same. 20 more pieces can be processed per day, so the profit increases by 10,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yen, sales 10,000 yen, profit 500 yen per piece
A2: The profit of 500 yen per rough stone remains the same. 20 more pieces can be processed per day, so the profit increases by 10,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yen, sales 10,000 yen, profit 500 yen per piece
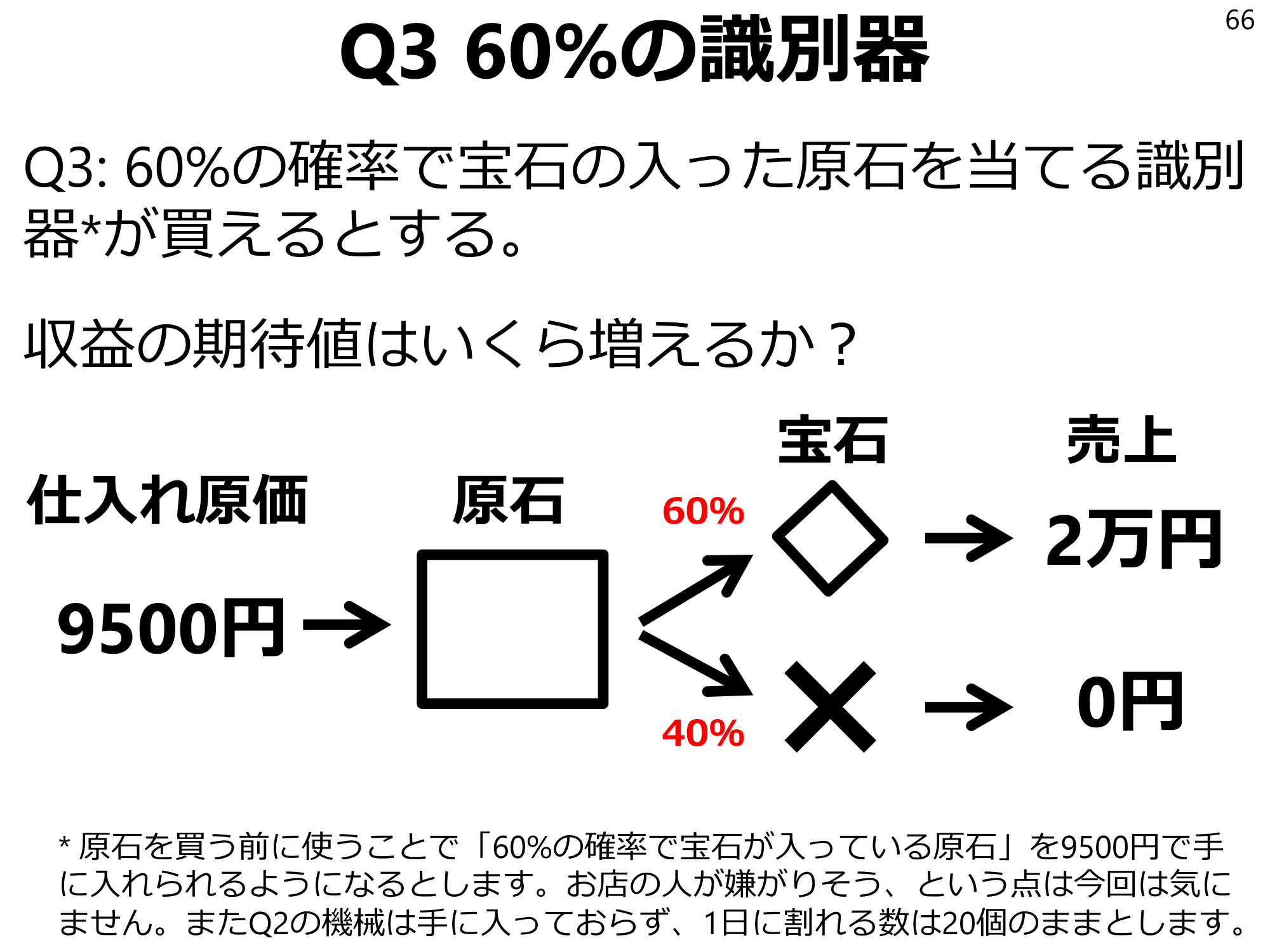 Q3 60% discriminator66 Q3: Suppose you can buy a discriminator* that has a 60% chance of hitting a gemstone with a gem in it. How much would the expected value of revenue increase? Purchase cost 60% gemstone 9500 yen x 40% sales 20,000 yen 0 yen* Suppose that by using it before buying a gemstone, you can get a “gemstone with a 60% chance of containing a gemstone” for 9500 yen. We do not care this time about the fact that the shopkeeper may not like it. Also, assume that the Q2 machine has not been obtained and that the number of gems that can be broken per day remains at 20.
Q3 60% discriminator66 Q3: Suppose you can buy a discriminator* that has a 60% chance of hitting a gemstone with a gem in it. How much would the expected value of revenue increase? Purchase cost 60% gemstone 9500 yen x 40% sales 20,000 yen 0 yen* Suppose that by using it before buying a gemstone, you can get a “gemstone with a 60% chance of containing a gemstone” for 9500 yen. We do not care this time about the fact that the shopkeeper may not like it. Also, assume that the Q2 machine has not been obtained and that the number of gems that can be broken per day remains at 20.
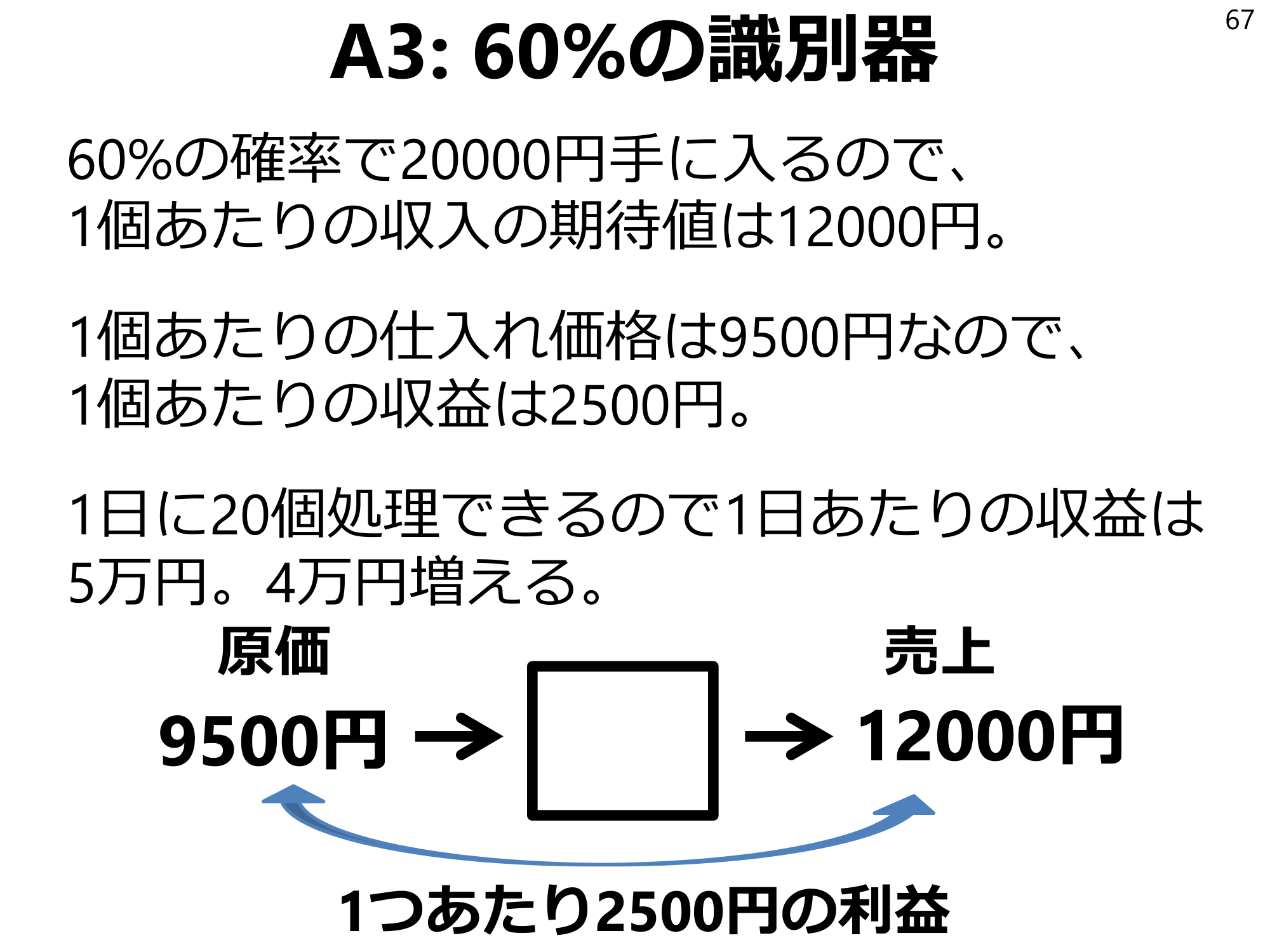 A3: 60% discriminator67 Since there is a 60% chance of getting 20,000 yen, the expected income per unit is 12,000 yen. the purchase price per unit is 9,500 yen, so the revenue per unit is 2,500 yen. since 20 units can be processed per day, the revenue per day is 50,000 yen. the revenue per unit increases by 40,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yenSales 12,000 yenProfit of 2,500 yen per unit
A3: 60% discriminator67 Since there is a 60% chance of getting 20,000 yen, the expected income per unit is 12,000 yen. the purchase price per unit is 9,500 yen, so the revenue per unit is 2,500 yen. since 20 units can be processed per day, the revenue per day is 50,000 yen. the revenue per unit increases by 40,000 yen. Cost 9,500 yenSales 12,000 yenProfit of 2,500 yen per unit
 In other words,68 in this problem set-up, “a device that doubles the processing speed” increases the customer’s profit by 10,000 yen, and “a discriminator with 60% accuracy” increases the customer’s profit by 40,000 yen. The “identifier with 60% accuracy” has four times the customer value of the “device that doubles the machining speed.
In other words,68 in this problem set-up, “a device that doubles the processing speed” increases the customer’s profit by 10,000 yen, and “a discriminator with 60% accuracy” increases the customer’s profit by 40,000 yen. The “identifier with 60% accuracy” has four times the customer value of the “device that doubles the machining speed.
 Summary69 -Customer value is important from a business perspective -Customer value is not “novelty of method” -Customer value does not equal accuracy
Summary69 -Customer value is important from a business perspective -Customer value is not “novelty of method” -Customer value does not equal accuracy
 Forced Open Innovation 70 -In 2017, Apple published its first machine learning paper -Even Apple can no longer say no to employee requests to publish -Machine learning technology cannot be a closed monopoly. - “Open innovation is not an option. It is a fact. “**Originally published in 2009 by Secretary of State Rice “Globalization is not a choice but a fact.”
Forced Open Innovation 70 -In 2017, Apple published its first machine learning paper -Even Apple can no longer say no to employee requests to publish -Machine learning technology cannot be a closed monopoly. - “Open innovation is not an option. It is a fact. “**Originally published in 2009 by Secretary of State Rice “Globalization is not a choice but a fact.”
 Market Procurement of Expertise71Many companies are looking to market procure expertise, but expert capabilities are difficult to observe and evaluate…(I’m going to tell you a terrible story off the record here.)
Market Procurement of Expertise71Many companies are looking to market procure expertise, but expert capabilities are difficult to observe and evaluate…(I’m going to tell you a terrible story off the record here.)
 Contract Theory72What is the solution when there is information asymmetry between contracting parties - signaling - screening
Contract Theory72What is the solution when there is information asymmetry between contracting parties - signaling - screening
 Signaling73 is an action taken by the side that has information. For example, “ability” tries to acquire “signals” that can indicate “ability” there difficult to observe
Signaling73 is an action taken by the side that has information. For example, “ability” tries to acquire “signals” that can indicate “ability” there difficult to observe
 Signaling74Why do Apple employees want to publish papers? It is because a track record of publishing papers is a “signal” and an advantage when changing jobs outside of Apple. When sourcing experts in the market, those experts are likely to demand that they can produce a signal.
Signaling74Why do Apple employees want to publish papers? It is because a track record of publishing papers is a “signal” and an advantage when changing jobs outside of Apple. When sourcing experts in the market, those experts are likely to demand that they can produce a signal.
 Screening75An action taken by the side that does not have the information. For example, offer a “low fixed salary + commission” to salespeople. Salespeople with low ability will avoid it on their own. However…
Screening75An action taken by the side that does not have the information. For example, offer a “low fixed salary + commission” to salespeople. Salespeople with low ability will avoid it on their own. However…
 Machine Learning and Pay-for-Performance76Machine learning has a characteristic that is incompatible with pay-for-performance: “You don’t know if you will get results until you try it on real data. Machine learning experts do not want to take on projects that pay for results. (If the data provided by the business side is dirty, the project will fail to produce results regardless of one’s ability.
Machine Learning and Pay-for-Performance76Machine learning has a characteristic that is incompatible with pay-for-performance: “You don’t know if you will get results until you try it on real data. Machine learning experts do not want to take on projects that pay for results. (If the data provided by the business side is dirty, the project will fail to produce results regardless of one’s ability.
 We need to find a contract structure that will benefit the smallest start 77 and the most competent professionals. Although a complete solution has not yet been devised, one idea is to make the first step of the contract small and extend it if both parties agree that it will work out well. The experts would not be locked in to a bad project for a long period of time, and the more competent ones would have a better chance of getting an extension.
We need to find a contract structure that will benefit the smallest start 77 and the most competent professionals. Although a complete solution has not yet been devised, one idea is to make the first step of the contract small and extend it if both parties agree that it will work out well. The experts would not be locked in to a bad project for a long period of time, and the more competent ones would have a better chance of getting an extension.
 Revenue Sharing78 Another strategy is revenue sharing, a method of sharing a fixed percentage of the profit generated by a project with a professional. Both parties cooperate in making a profit. However, it is difficult for the expert to accept a revenue-sharing contract alone because the results will vary depending on the capabilities of the project manager in addition to his or her own skills.
Revenue Sharing78 Another strategy is revenue sharing, a method of sharing a fixed percentage of the profit generated by a project with a professional. Both parties cooperate in making a profit. However, it is difficult for the expert to accept a revenue-sharing contract alone because the results will vary depending on the capabilities of the project manager in addition to his or her own skills.
 Summary79 - Forced open innovation - Information asymmetry issues arise in market procurement of specialized skills - Contract theory offers useful suggestions for better contracts
Summary79 - Forced open innovation - Information asymmetry issues arise in market procurement of specialized skills - Contract theory offers useful suggestions for better contracts
 Overall Summary 80 -Do not make the means an end. -AI does not take away jobs but augments humans = reduced time cost paid by humans -Difference in evaluation axes between academia and business. Customer value ≠ novelty/precision
Overall Summary 80 -Do not make the means an end. -AI does not take away jobs but augments humans = reduced time cost paid by humans -Difference in evaluation axes between academia and business. Customer value ≠ novelty/precision
This page is auto-translated from /nishio/東工大ホームカミングデー「AIとMOT」 using DeepL. If you looks something interesting but the auto-translated English is not good enough to understand it, feel free to let me know at @nishio_en. I’m very happy to spread my thought to non-Japanese readers.